Assignments - Computer Communication And Networking
1. What is a "Computer Network"?
A computer network is a system that connects many independent computers to share information (data) and resources. The integration of computers and other different devices allows users to communicate more easily. A computer network is a collection of two or more computer systems that are linked together. (1)
2. Explain some Applications of Computer Networking.
Computer networking has a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where it plays a crucial role:
Internet Connectivity: The most obvious application is connecting devices to the internet, enabling access to online resources, communication, and services.
Communication: Networking facilitates email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and VoIP, allowing for real-time communication across the globe.
Web Services: Networking is essential for hosting and accessing websites, web applications, and services, driving e-commerce and online businesses.
IoT (Internet of Things): Computer networking connects smart devices, enabling automation and data exchange in homes and industries, improving efficiency and control.
Cloud Computing: Networking underpins cloud services, allowing users to access applications and data stored on remote servers rather than on local machines.
Social Networking: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn rely on computer networking to connect users, facilitating social interactions and information sharing.
Security Systems: Networking is crucial for connecting surveillance cameras and alarm systems, allowing for remote monitoring and management of security.
Healthcare: In medical settings, networks facilitate electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and real-time patient monitoring, improving patient care.
Education: Educational institutions use networking for e-learning platforms, online classes, and virtual labs, making education more accessible.
Each of these applications highlights the importance of computer networking in enhancing connectivity, collaboration, and efficiency in modern life. (1)
3. What is a "Network Topology"? Explain types with neat diagram.
Network Topology refers to the arrangement or layout of different elements (links, nodes, etc.) in a computer network. It defines how devices are interconnected and how data flows within the network. Understanding network topology is essential for designing and managing networks effectively. Here are the primary types of network topologies:
1. Bus Topology
- All devices share a single communication line (the bus). Data sent by any device travels in both directions along the bus until it reaches its destination.
2. Star Topology
- All devices are connected to a central hub or switch. Data is sent from one device to the hub, which then forwards it to the intended recipient.

3. Ring Topology
- Each device is connected to two other devices, forming a circular pathway for data. Data travels in one direction (or both, in some variations) until it reaches its destination.

4. Mesh Topology
- Every device is connected to every other device, either fully (every device is connected) or partially (some devices are interconnected).

5. Tree Topology
- A hybrid topology that combines characteristics of star and bus topologies. It has a central hub (like star) with multiple levels of hierarchy, forming a tree-like structure. (1) (2)

4. Explain Types of Networks with Advantages and Disadvantages.
Networks can be classified into several types based on their size, scope, and purpose. Here are the main types of networks, along with their advantages and disadvantages:
1. Local Area Network (LAN)
- Definition: A network that covers a small geographic area, like a single building or campus.
- Advantages:
- High-speed data transfer.
- Low cost for setting up and maintaining.
- Easy to connect devices and share resources (like printers and files).
- Disadvantages:
- Limited range; not suitable for large distances.
- Security risks if not properly managed.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Definition: A network that spans a large geographic area, such as cities or countries, often using leased telecommunication lines.
- Advantages:
- Can connect multiple LANs over long distances.
- Facilitates communication across large geographical areas.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher costs for setup and maintenance.
- Slower data transfer speeds compared to LANs.
- More complex management and security considerations.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Definition: A network that covers a city or a large campus, typically larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- Advantages:
- Higher speeds than WANs due to shorter distances.
- Ideal for connecting multiple LANs in a specific area.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be expensive to set up and maintain.
- Limited to metropolitan areas. (1)
5. Explain the TCP/IP Model with a neat diagram for reference.
The TCP/IP model is a fundamental framework for computer networking. It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, which are the core protocols of the Internet. This model defines how data is transmitted over networks, ensuring reliable communication between devices. It consists of four layers: the Link Layer, the Internet Layer, the Transport Layer, and the Application Layer. Each layer has specific functions that help manage different aspects of network communication, making it essential for understanding and working with modern networks. (1)
6. What is a "Transmission Medium"? Explain its Types.
Transmission media refers to the physical medium through which data is transmitted from one device to another within a network. These medium can be wired or wireless. The choice of medium depends on factors like distance, speed, and interference. A transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e. it is the channel through which data is sent from one device to another. (1) Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
- Guided Media
- Guided Media is also referred to as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links.
- Unguided Media
- It is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media . No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
7. Explain Twisted Pair Cables with a neat diagram.
Twisted Pair Cable is a type of wiring used for transmitting data in telecommunications and networking. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell. Twisted pair cables have two conductors that are generally made up of copper and each conductor has insulation. These two conductors are twisted together, thus giving the name twisted pair cables. (1) (2)
- Twisted Pair Cables are further of two types :
- Unshielded Twisted Pair Cables (UTP)
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)

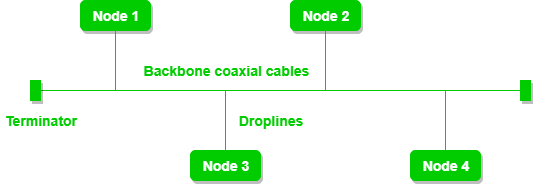
8. Explain Coaxial Cables with a neat diagram.
Coaxial Cable is a type of guided media made of Plastics, and copper wires which transmit the signal in electrical form rather than light form. Coaxial cable is also known as coax. The core copper conductor is used for the transmission of signals and the insulator is used to provide insulation to the copper conductor the insulator is surrounded by a braided metal conductor which helps to prevent the interference of electrical signals and prevent cross talk. This entire setup is again covered with a protective plastic layer to provide extra safety to the cable. (1)
9. Explain Optical Fibre Cables with a neat diagram.
Optical fiber is a technology used to transmit data by sending short light pulses along a long fiber, which is typically made of glass or plastic. In optical fiber communication, metal wires are preferred for transmission because the signals travel more safely. Optical fibers are also resistant to electromagnetic interference. Total internal reflection of light is used in the fiber optical cable. Depending on the amount of power needed and the distance needed, the fibers are designed to allow light to travel in parallel with the optical fiber. While multimode fiber is used for transmission over shorter distances, single-mode fiber is used for long-distance transmission. These fibers’ outer covering requires better defense than metal wires can provide. (1)
10. Write a note on Radio Waves, Microwaves and IR Waves each.
1. Radiowave Transmission
The radio waves have frequency range from 3 KHz to 1 GHz. These waves are easy to generate and these can travel along long distances. These waves are omni directional in nature which means that they can travel in all the directions. They are widely used for the communication between both indoor and outdoor because they have the property that they can penetrate through the walls very easily. These waves are usually used for AM and FM radio, television, cellular phones and wireless LAN.
2. Microwave Transmission
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves which have frequency range between 1 GHz to 300 GHz. These can travel along long distances. These are unidirectional in nature which means that they can travel only in straight line. At very high frequency that cannot penetrate into walls. These waves are usually used for one to one communication between sender and receiver, cellular phones, satellite networks, and wireless LAN.
3. Infrared Waves
Infrared Waves are electromagnetic waves that have frequency range between 300 GHz to 400 THz. These cannot travel along long distances. These waves are used for short range communication and they also use line-of-sight of propagation. These waves cannot pass through solid objects like walls etc. These also not penetrate through walls. The most common application of the IR waves is remote controls that are used for TV, DVD players, and stereo system.
11. What is "Switching"? Explain Types of Switching.
Switching is a technique used in computer networking to direct data packets between devices on a network. It involves receiving incoming packets and determining the best path for them to reach their destination. The main types of switching are:
1. Circuit Switching
- A dedicated communication path is established between two endpoints for the duration of the communication session.
2. Packet Switching
- Data is broken into smaller packets that are sent independently over the network. Each packet may take a different route to reach the destination, where they are reassembled.
3. Message Switching
- Entire messages are sent to a switch, stored temporarily, and then forwarded to the next hop. Each message is processed one at a time. (1)
12. What is "Multiplexing"?
Multiplexing is a technique used to combine and send the multiple data streams over a single medium. The process of combining the data streams is known as multiplexing and hardware used for multiplexing is known as a multiplexer.
Multiplexing is achieved by using a device called Multiplexer (MUX) that combines n input lines to generate a single output line. Multiplexing follows many-to-one, i.e., n input lines and one output line. (1)