Unit 1: Introduction
Important Questions
Q1.What is network topology? Explain different types of topology
Network topology refers to the way that nodes and connections are physically and logically arranged in a network.
Networks consist of a series of links and nodes. Nodes include devices like routers, switchers, repeaters, and computers.
A network topology describes how these components are arranged in relation to each other and how data moves through the network.

Point to Point Topology
Point to point connects two nodes, in which one is the sender and the other one is the receiver.
Point-to-Point provides high bandwidth.

Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via a particular channel.
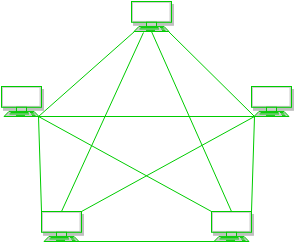
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- Communication is very fast between the nodes.
- Mesh Topology is robust.
- The fault is diagnosed easily. Data is reliable because data is transferred among the devices through dedicated channels or links.
- Provides security and privacy.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- Installation and configuration are difficult.
- The cost of cables is high as bulk wiring is required, hence suitable for less number of devices.
- The cost of maintenance is high.
Star Topology
In Star Topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable.
This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node

Advantages of Star Topology:
- If N devices are connected to each other in a star topology, then the number of cables required to connec- them is N. So, it is easy to set up.
- Each device requires only 1 port i.e. to connect to the hub, therefore the total number of ports required is N.
- It is Robust. If one link fails only that link will affect and not other than that.
- Easy to fault identification and fault isolation.
- Star topology is cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- If the concentrator (hub) on which the whole topology relies fails, the whole system will crash down.
- The cost of installation is high.
- Performance is based on the single concentrator i.e. hub.
Bus Topology
Bus Topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to a single cable.
It is bi-directional.
It is a multi-point connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails the topology crashes.
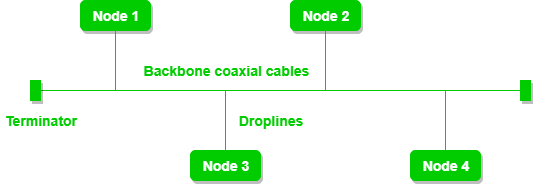
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- If N devices are connected to each other in a bus topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is 1, known as backbone cable, and N drop lines are required.
- Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support up to 10 Mbps.
- The cost of the cable is less compared to other topologies, but it is used to build small networks.
- Bus topology is familiar technology as installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known.
- CSMA is the most common method for this type of topology.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:
- A bus topology is quite simpler, but still, it requires a lot of cabling.
- If the common cable fails, then the whole system will crash down.
- If the network traffic is heavy, it increases collisions in the network. To avoid this, various protocols are used in the MAC layer known as Pure Aloha, Slotted Aloha, CSMA/CD, etc.
- Adding new devices to the network would slow down networks.
- Security is very low.
Ring Topology
In a Ring Topology, it forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices.
A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with a large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss, repeaters are used in the network.
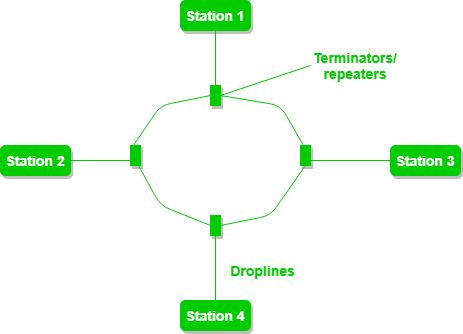
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- The data transmission is high-speed.
- The possibility of collision is minimum in this type of topology.
- Cheap to install and expand.
- It is less costly than a star topology.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
- The failure of a single node in the network can cause the entire network to fail.
- Troubleshooting is difficult in this topology.
- The addition of stations in between or the removal of stations can disturb the whole topology.
- Less secure.
Tree Topology
Tree Topology is a variation of the Star topology. This topology has a hierarchical flow of data.

Advantages of Tree Topology:
- It allows more devices to be attached to a single central hub thus it decreases the distance that is traveled by the signal to come to the devices.
- It allows the network to get isolated and also prioritize from different computers.
- We can add new devices to the existing network.
- Error detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
- If the central hub gets fails the entire system fails.
- The cost is high because of the cabling.
- If new devices are added, it becomes difficult to reconfigure.
Hybrid Topology
This topological technology is the combination of all the various types of topologies we have seen above.
Hybrid Topology is used when the nodes are free to take any form.
It means these can be individuals such as Ring or Star topology or can be a combination of various types of topologies seen above. Each individual topology uses the protocol that has been shown earlier.

Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- This topology is very flexible .
- The size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
It is challenging to design the architecture of the Hybrid Network.
Hubs used in this topology are very expensive.
The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling and network devices .
Q2.Write a note on:
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN is a computer network that spans a small geographical area, typically within a building or campus. It connects devices such as computers, printers, and servers, allowing them to communicate and share resources.
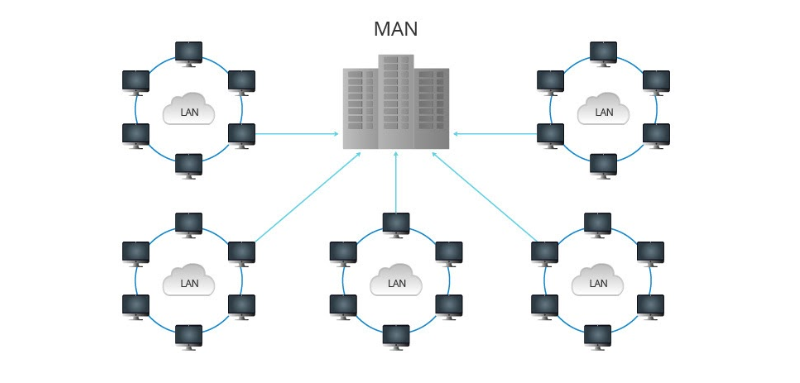
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
A MAN is a computer network that covers a larger geographical area than a LAN, typically a metropolitan area or city. It is used to connect multiple LANs and provide internet access, telecommunication services, and other applications.
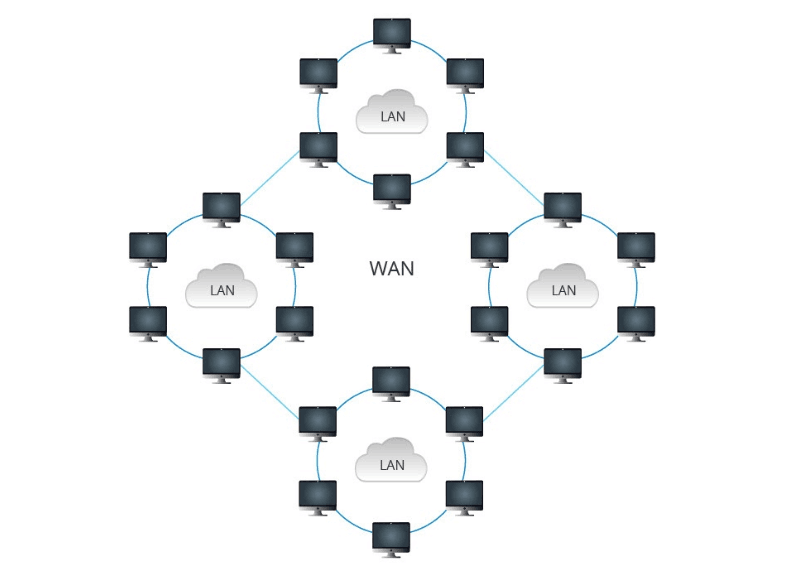
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN is a computer network that covers a large geographical area, often spanning multiple cities, states, or even countries. It is used to connect multiple LANs and MANs, providing long-distance communication and data transfer services.
Q3. Explain OSI model with a neat diagram
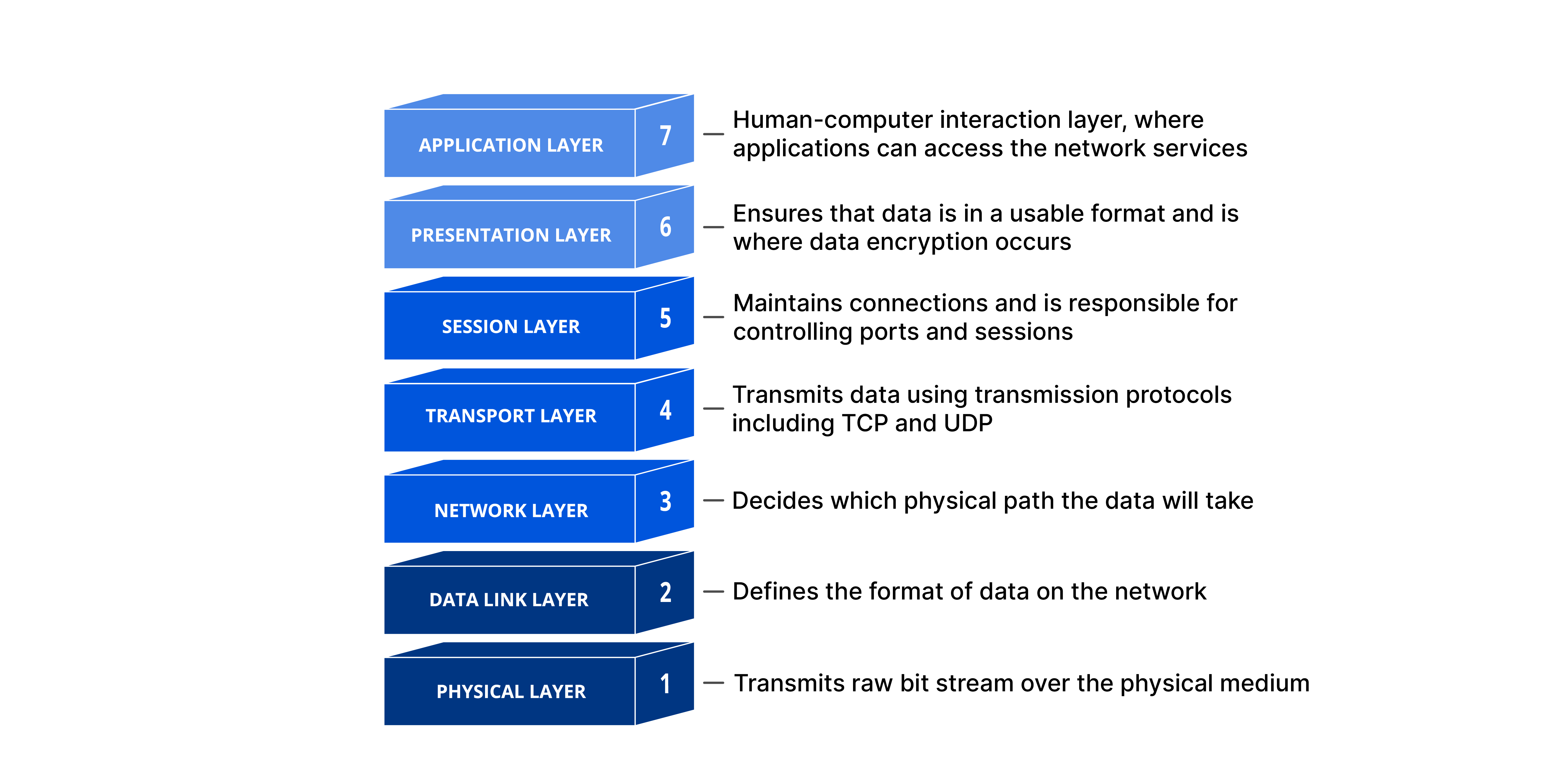
The OSI Model provides a standard for different computer systems to be able to communicate with each other.
The OSI Model can be seen as a universal language for computer networking. It is based on the concept of splitting up a communication system into seven abstract layers, each one stacked upon the last.
Although the modern Internet does not strictly follow the OSI Model (it more closely follows the simpler Internet protocol suite), the OSI Model is still very useful.
It is made up of 7 layers:
- Application Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Session Layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
- Data link layer
- Physical layer
What are the 7 layers of the OSI Model?
The seven abstraction layers of the OSI model can be defined as follows, from top to bottom:
- Application Layer
- This is the only layer that directly interacts with data from the user.
- The application layer is responsible for the protocols and data manipulation that the software relies on to present data to the user.
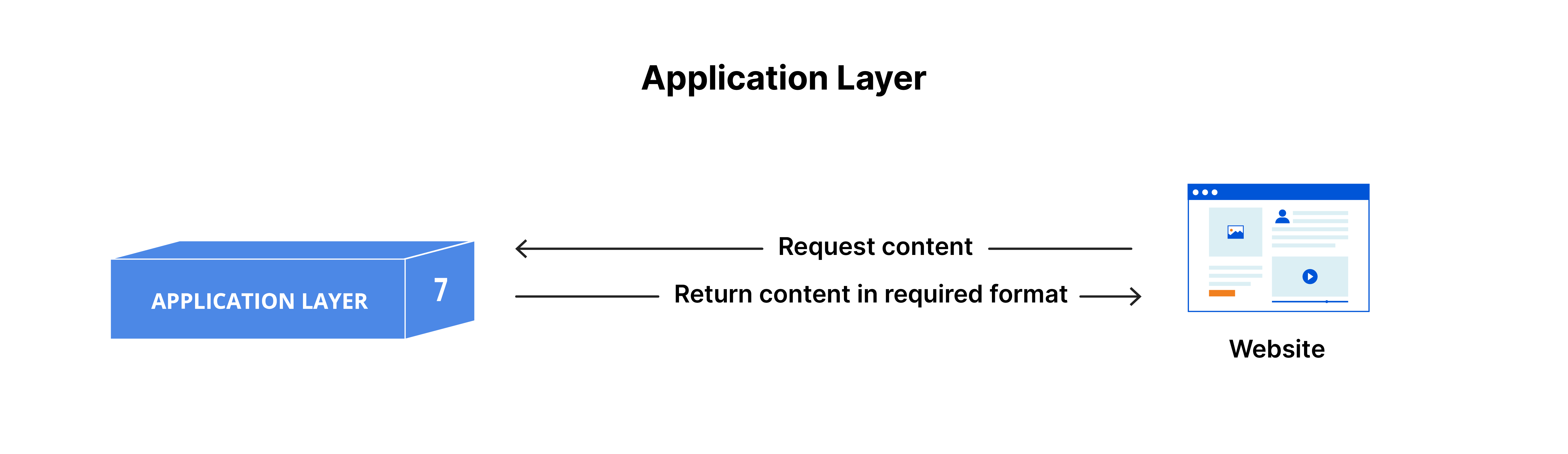
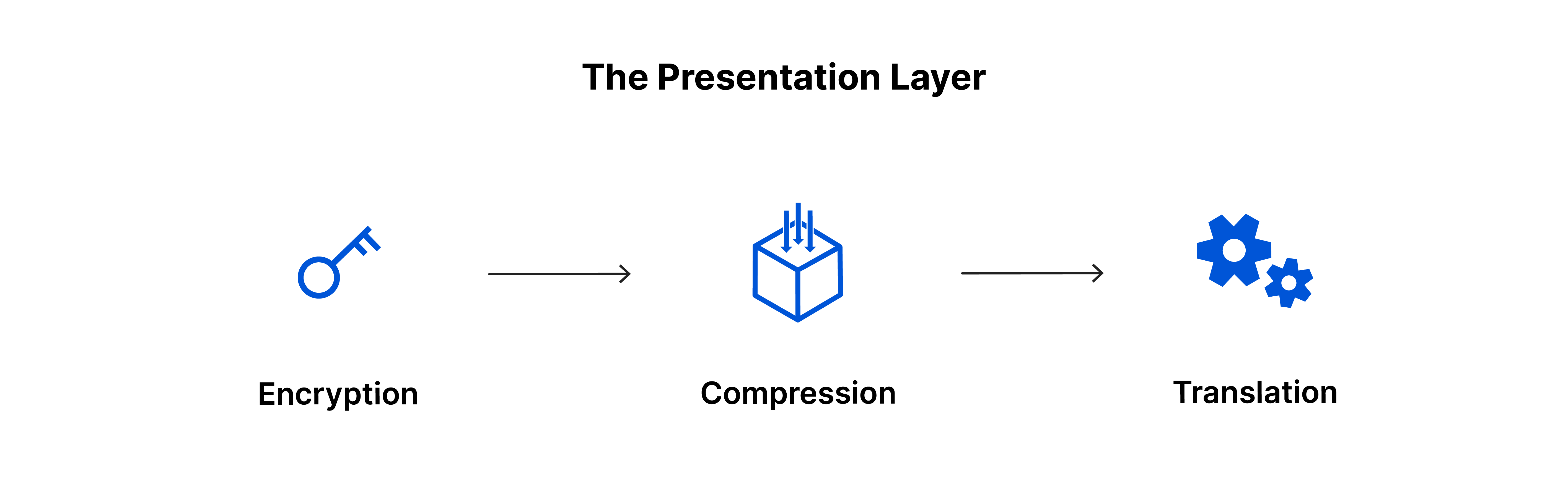
- The presentation layer
- This layer is primarily responsible for preparing data so that it can be used by the application layer
- The presentation layer is responsible for translation, encryption, and compression of data.
- The session layer
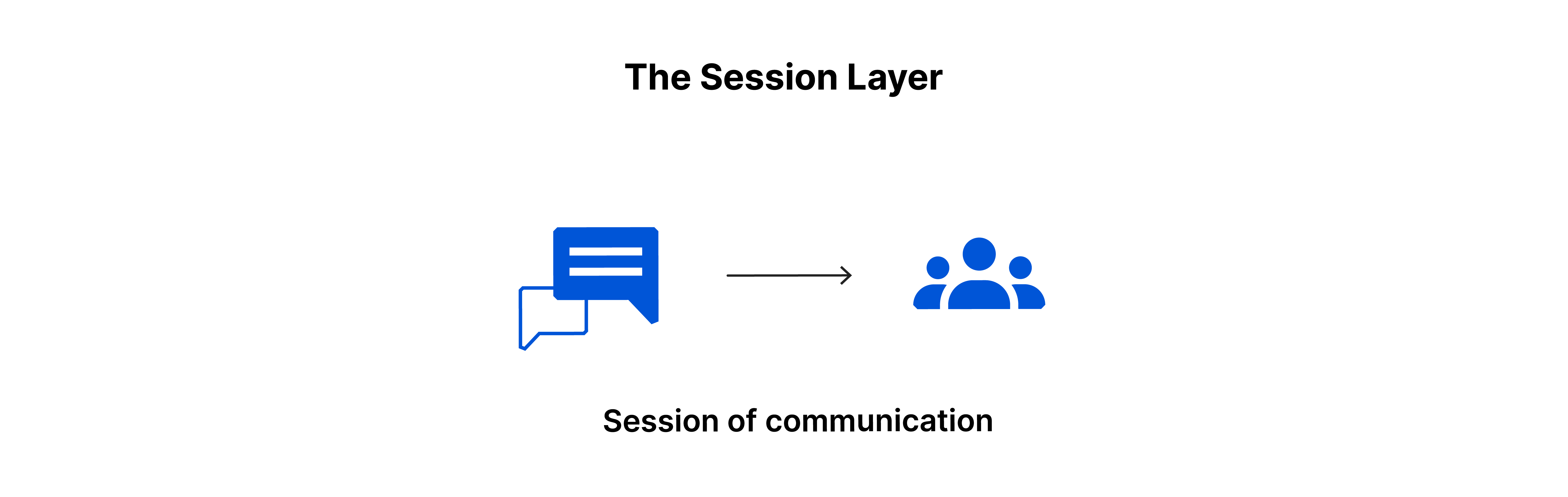
- This is the layer responsible for opening and closing communication between the two devices.
- The time between when the communication is opened and closed is known as the session.
- The session layer ensures that the session stays open long enough to transfer all the data being exchanged, and then promptly closes the session in order to avoid wasting resources.
- The transport layer
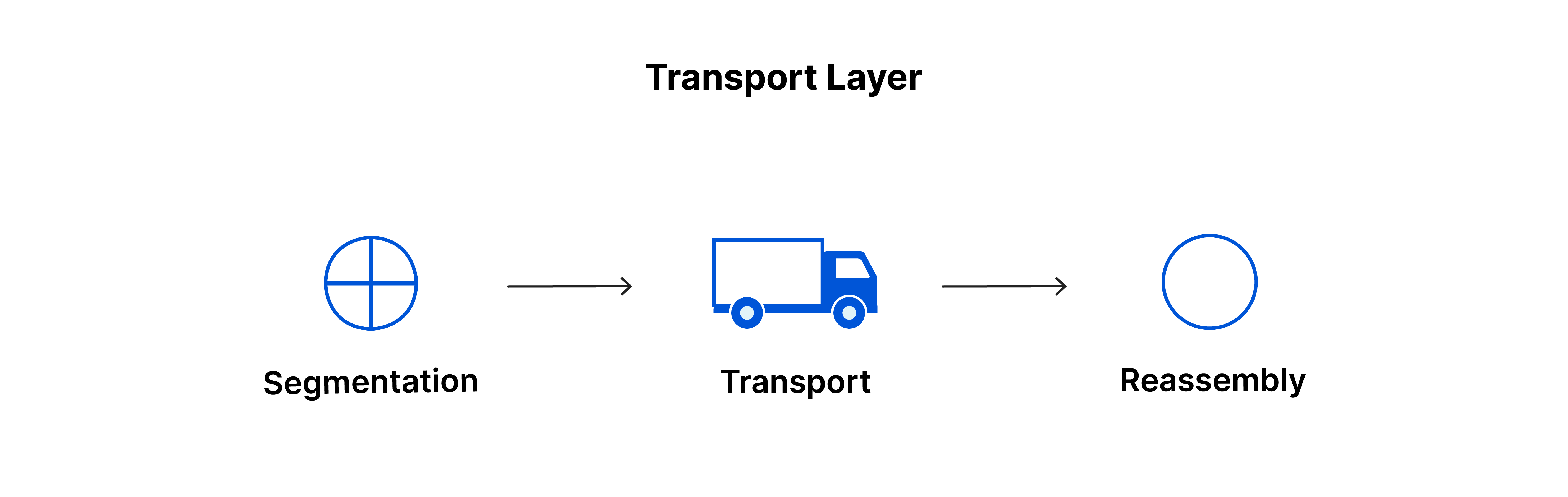
- is responsible for end-to-end communication between the two devices.
- This includes taking data from the session layer and breaking it up into chunks called segments before sending it to the network layer.
- The transport layer on the receiving device is responsible for reassembling the segments into data the session layer can consume.
- The network layer
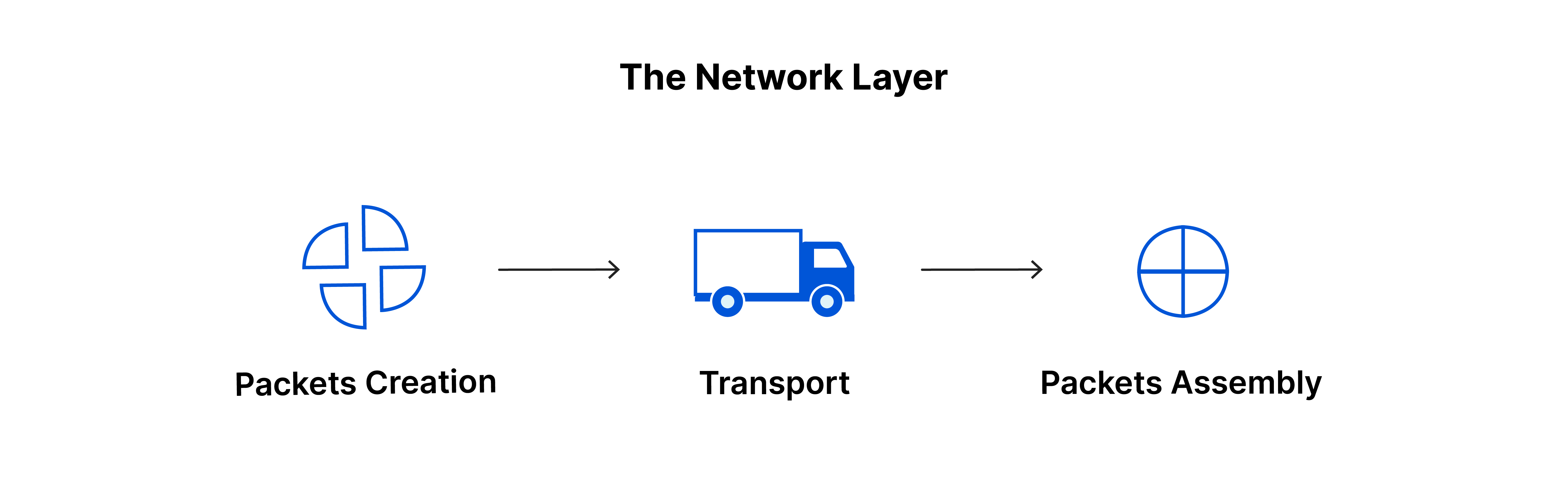
- The network layer is responsible for facilitating data transfer between two different networks.
- The network layer breaks up segments from the transport layer into smaller units on the sender’s device(called packets), and reassembling these packets on the receiving device.
- The data link layer
- The data link layer is very similar to the network layer, except the data link layer facilitates data transfer between two devices on the same network.
- The data link layer takes packets from the network layer and breaks them into smaller pieces called frames
- The physical layer
- The physical layer includes the physical equipment involved in the data transfer, such as the cables and switches.
- This is also the layer where the data gets converted into a bit stream, which is a string of 1s and 0s.
Q4. Write a note on TCP/IP
TCP/IP Model stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, which are the core protocols of the Internet.
This model defines how data is transmitted over networks, ensuring reliable communication between devices.
It consists of four layers:
- the Link Layer
- Defines how data is sent over a physical network
- the Internet Layer
- Routes packets between networks using IP
- the Transport Layer
- Provides reliable data transfer between devices using TCP or UDP
- the Application Layer
- Supports protocols and functions for email, file transfer, web browsing, games, etc

Q5. Explain application of computer networks in detail
Here are some applications of Computer Networks:
Communication and Information Sharing
- Email: Send and receive emails over the internet
- Instant Messaging: Real-time communication using platforms like WhatsApp, Slack, etc.
- File Sharing: Share files and documents between devices and users
- Resource Sharing: Share hardware resources like printers, scanners, and servers
Remote Work, Education, and Entertainment
- Telecommuting: Work from home or remote locations using virtual private networks (VPNs)
- Online Courses: Take online courses and access educational resources
- Online Gaming: Play online games with users from around the world
- Streaming Services: Stream music, videos, and movies using services like Netflix, Hulu, etc.
Commerce, Healthcare, and Security
- E-commerce: Buy and sell products online using e-commerce websites
- Online Banking: Conduct online banking and financial transactions
- Telemedicine: Consult doctors and access medical services remotely
- Network Security: Protect computer networks from cyber threats and attacks
Q6. What is communication?
Communication is when 2 or more parties share data between each other.
Q7. Wat is a computer network?
A computer network is when multiple computers are linked to each other to share resources, exchange files, or allow communication.
Q8. What is the physical layer?
The physical Layer is the bottom-most layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model.
It deals with switches and cables that connect the computers together. We can observe various topologies here like BUS topology, MESH topology, Star topology, etc
Q9. Explain layers of TCP/ip model
TCP/IP Model has the following layers:
- Appliation Layer
- Transport Layer
- The TCP/IP transport layer protocols exchange data receipt acknowledgments and retransmit missing packets to ensure that packets arrive in order and without error
- TCP: Applications can interact with one another using TCP as though they were physically connected by a circuit
- UDP: The datagram delivery service is provided by UDP, the other transport layer protocol.
- TCP ensures that data is delivered reliably, while UDP does not(so it is faster).
- TCP retransmits lost or damaged packets, while UDP drops them and moves on
- Network Layer
- This layer parallels the functions of OSI’s Network layer.
- It defines the protocols which are responsible for the logical transmission of data over the entire network
- The main protocols residing at this layer are as follows:
- IP: IP stands for Internet Protocol and it is responsible for delivering packets from the source host to the destination host by looking at the IP addresses in the packet headers.
- ICMP: ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol used to manage errors and provide information about IP networks.
- ARP: ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. Its job is to find the hardware address of a host from a known IP address
- Network Access Layer
- This layer is responsible for generating the data and requesting connections
Q10. What are the Advantages and disadvantages of topology
Answered in Q1
Source:
- Questions: Dictated in class